稀疏资源
绑定稀疏内存
与调用 vkBindBufferMemory() 或 vkBindImageMemory() 的普通资源不同,稀疏内存通过 队列操作 vkQueueBindSparse() 绑定。这样做的好处是,应用程序可以在其生命周期内重新绑定到稀疏资源的内存。
重要的是要注意,这需要应用程序进行一些额外的考虑。应用程序必须使用同步原语来保证其他队列不会与绑定更改同时访问内存范围。此外,使用 vkFreeMemory() 释放 VkDeviceMemory 对象不会导致绑定到该内存对象的资源(或资源区域)解除绑定。应用程序不得访问绑定到已释放内存的资源。
稀疏缓冲区
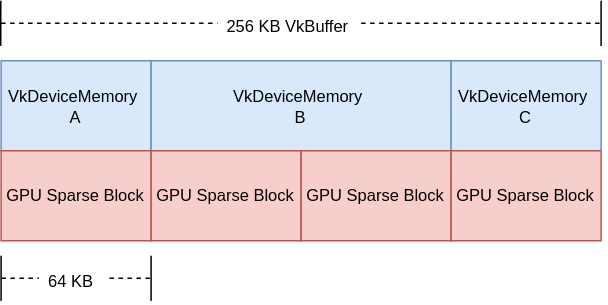
以下示例用于帮助直观地展示稀疏的 VkBuffer 在内存中的外观。请注意,这不是必需的,但大多数实现将使用 64 KB 的稀疏块大小用于 VkBuffer (实际大小在 VkMemoryRequirements::alignment 中返回)。
假设一个 256 KB 的 VkBuffer,其中有 3 个部分应用程序想要单独更新。
-
A 部分 - 64 KB
-
B 部分 - 128 KB
-
C 部分 - 64 KB
以下展示了应用程序如何查看 VkBuffer
稀疏图像
Mip 尾部区域
稀疏图像可以用来单独更新 mip 级别,从而产生一个 mip 尾部区域。规范用图表描述了可能发生的各种示例。
基本稀疏资源示例
以下示例说明了稀疏图像的基本创建以及将它们绑定到物理内存的过程。
此基本示例创建一个普通的 VkImage 对象,但使用细粒度的内存分配来使用多个内存范围来支持资源。
VkDevice device;
VkQueue queue;
VkImage sparseImage;
VkAllocationCallbacks* pAllocator = NULL;
VkMemoryRequirements memoryRequirements = {};
VkDeviceSize offset = 0;
VkSparseMemoryBind binds[MAX_CHUNKS] = {}; // MAX_CHUNKS is NOT part of Vulkan
uint32_t bindCount = 0;
// ...
// Allocate image object
const VkImageCreateInfo sparseImageInfo =
{
VK_STRUCTURE_TYPE_IMAGE_CREATE_INFO, // sType
NULL, // pNext
VK_IMAGE_CREATE_SPARSE_BINDING_BIT | ..., // flags
...
};
vkCreateImage(device, &sparseImageInfo, pAllocator, &sparseImage);
// Get memory requirements
vkGetImageMemoryRequirements(
device,
sparseImage,
&memoryRequirements);
// Bind memory in fine-grained fashion, find available memory ranges
// from potentially multiple VkDeviceMemory pools.
// (Illustration purposes only, can be optimized for perf)
while (memoryRequirements.size && bindCount < MAX_CHUNKS)
{
VkSparseMemoryBind* pBind = &binds[bindCount];
pBind->resourceOffset = offset;
AllocateOrGetMemoryRange(
device,
&memoryRequirements,
&pBind->memory,
&pBind->memoryOffset,
&pBind->size);
// memory ranges must be sized as multiples of the alignment
assert(IsMultiple(pBind->size, memoryRequirements.alignment));
assert(IsMultiple(pBind->memoryOffset, memoryRequirements.alignment));
memoryRequirements.size -= pBind->size;
offset += pBind->size;
bindCount++;
}
// Ensure entire image has backing
if (memoryRequirements.size)
{
// Error condition - too many chunks
}
const VkSparseImageOpaqueMemoryBindInfo opaqueBindInfo =
{
sparseImage, // image
bindCount, // bindCount
binds // pBinds
};
const VkBindSparseInfo bindSparseInfo =
{
VK_STRUCTURE_TYPE_BIND_SPARSE_INFO, // sType
NULL, // pNext
...
1, // imageOpaqueBindCount
&opaqueBindInfo, // pImageOpaqueBinds
...
};
// vkQueueBindSparse is externally synchronized per queue object.
AcquireQueueOwnership(queue);
// Actually bind memory
vkQueueBindSparse(queue, 1, &bindSparseInfo, VK_NULL_HANDLE);
ReleaseQueueOwnership(queue);高级稀疏资源
这个更高级的示例创建一个阵列化的颜色附件/纹理图像,并且只将 LOD 零和所需的元数据绑定到物理内存。
VkDevice device;
VkQueue queue;
VkImage sparseImage;
VkAllocationCallbacks* pAllocator = NULL;
VkMemoryRequirements memoryRequirements = {};
uint32_t sparseRequirementsCount = 0;
VkSparseImageMemoryRequirements* pSparseReqs = NULL;
VkSparseMemoryBind binds[MY_IMAGE_ARRAY_SIZE] = {};
VkSparseImageMemoryBind imageBinds[MY_IMAGE_ARRAY_SIZE] = {};
uint32_t bindCount = 0;
// Allocate image object (both renderable and sampleable)
const VkImageCreateInfo sparseImageInfo =
{
VK_STRUCTURE_TYPE_IMAGE_CREATE_INFO, // sType
NULL, // pNext
VK_IMAGE_CREATE_SPARSE_RESIDENCY_BIT | ..., // flags
...
VK_FORMAT_R8G8B8A8_UNORM, // format
...
MY_IMAGE_ARRAY_SIZE, // arrayLayers
...
VK_IMAGE_USAGE_COLOR_ATTACHMENT_BIT |
VK_IMAGE_USAGE_SAMPLED_BIT, // usage
...
};
vkCreateImage(device, &sparseImageInfo, pAllocator, &sparseImage);
// Get memory requirements
vkGetImageMemoryRequirements(
device,
sparseImage,
&memoryRequirements);
// Get sparse image aspect properties
vkGetImageSparseMemoryRequirements(
device,
sparseImage,
&sparseRequirementsCount,
NULL);
pSparseReqs = (VkSparseImageMemoryRequirements*)
malloc(sparseRequirementsCount * sizeof(VkSparseImageMemoryRequirements));
vkGetImageSparseMemoryRequirements(
device,
sparseImage,
&sparseRequirementsCount,
pSparseReqs);
// Bind LOD level 0 and any required metadata to memory
for (uint32_t i = 0; i < sparseRequirementsCount; ++i)
{
if (pSparseReqs[i].formatProperties.aspectMask &
VK_IMAGE_ASPECT_METADATA_BIT)
{
// Metadata must not be combined with other aspects
assert(pSparseReqs[i].formatProperties.aspectMask ==
VK_IMAGE_ASPECT_METADATA_BIT);
if (pSparseReqs[i].formatProperties.flags &
VK_SPARSE_IMAGE_FORMAT_SINGLE_MIPTAIL_BIT)
{
VkSparseMemoryBind* pBind = &binds[bindCount];
pBind->memorySize = pSparseReqs[i].imageMipTailSize;
bindCount++;
// ... Allocate memory range
pBind->resourceOffset = pSparseReqs[i].imageMipTailOffset;
pBind->memoryOffset = /* allocated memoryOffset */;
pBind->memory = /* allocated memory */;
pBind->flags = VK_SPARSE_MEMORY_BIND_METADATA_BIT;
}
else
{
// Need a mip tail region per array layer.
for (uint32_t a = 0; a < sparseImageInfo.arrayLayers; ++a)
{
VkSparseMemoryBind* pBind = &binds[bindCount];
pBind->memorySize = pSparseReqs[i].imageMipTailSize;
bindCount++;
// ... Allocate memory range
pBind->resourceOffset = pSparseReqs[i].imageMipTailOffset +
(a * pSparseReqs[i].imageMipTailStride);
pBind->memoryOffset = /* allocated memoryOffset */;
pBind->memory = /* allocated memory */
pBind->flags = VK_SPARSE_MEMORY_BIND_METADATA_BIT;
}
}
}
else
{
// resource data
VkExtent3D lod0BlockSize =
{
AlignedDivide(
sparseImageInfo.extent.width,
pSparseReqs[i].formatProperties.imageGranularity.width);
AlignedDivide(
sparseImageInfo.extent.height,
pSparseReqs[i].formatProperties.imageGranularity.height);
AlignedDivide(
sparseImageInfo.extent.depth,
pSparseReqs[i].formatProperties.imageGranularity.depth);
}
size_t totalBlocks =
lod0BlockSize.width *
lod0BlockSize.height *
lod0BlockSize.depth;
// Each block is the same size as the alignment requirement,
// calculate total memory size for level 0
VkDeviceSize lod0MemSize = totalBlocks * memoryRequirements.alignment;
// Allocate memory for each array layer
for (uint32_t a = 0; a < sparseImageInfo.arrayLayers; ++a)
{
// ... Allocate memory range
VkSparseImageMemoryBind* pBind = &imageBinds[a];
pBind->subresource.aspectMask = pSparseReqs[i].formatProperties.aspectMask;
pBind->subresource.mipLevel = 0;
pBind->subresource.arrayLayer = a;
pBind->offset = (VkOffset3D){0, 0, 0};
pBind->extent = sparseImageInfo.extent;
pBind->memoryOffset = /* allocated memoryOffset */;
pBind->memory = /* allocated memory */;
pBind->flags = 0;
}
}
free(pSparseReqs);
}
const VkSparseImageOpaqueMemoryBindInfo opaqueBindInfo =
{
sparseImage, // image
bindCount, // bindCount
binds // pBinds
};
const VkSparseImageMemoryBindInfo imageBindInfo =
{
sparseImage, // image
sparseImageInfo.arrayLayers, // bindCount
imageBinds // pBinds
};
const VkBindSparseInfo bindSparseInfo =
{
VK_STRUCTURE_TYPE_BIND_SPARSE_INFO, // sType
NULL, // pNext
...
1, // imageOpaqueBindCount
&opaqueBindInfo, // pImageOpaqueBinds
1, // imageBindCount
&imageBindInfo, // pImageBinds
...
};
// vkQueueBindSparse is externally synchronized per queue object.
AcquireQueueOwnership(queue);
// Actually bind memory
vkQueueBindSparse(queue, 1, &bindSparseInfo, VK_NULL_HANDLE);
ReleaseQueueOwnership(queue);